李海涛 1,2,3赵波 2,***张祥志 1,3,4,**郭智 1,3,4[ ... ]邰仁忠 1,2,3,4,*
1 中国科学院上海高等研究院 上海 201210
2 上海科技大学 上海 201210
3 中国科学院上海应用物理研究所 上海 201800
4 中国科学院大学 北京 100049
同步辐射实验方法在研究材料的结构和物性上具有独特的优势,然而,要实现同步辐射原位高温条件,尤其温度高于2 000 K以上,对很多实验方法来说还是一个挑战。激光加热方法可以实现快速、微区的极端高温条件,已经成为高温物性研究的重要工具。上海同步辐射光源在极端高温研究领域,例如高熵合金、涡轮叶片、航空材料等还欠缺相关的原位高温条件,因此,研制了一种便携式连续激光加热装置,利用光谱仪获得样品的热辐射谱,并通过黑体辐射方法拟合出样品的温度梯度和温度稳定性。利用该装置成功实现真空环境中钨片的快速熔化(熔点约3 695 K),并在上海同步辐射光源表面衍射线站获得了1 608 K原位条件下的MoS2和CTAB-MoS2材料X射线衍射图谱。本工作所研制的激光加热方法拓展了上海光源在极端条件下的实验能力,为极端高温条件下的材料物性研究提供了重要手段。
激光加热 同步辐射 原位实验 X射线衍射 Laser heating Synchrotron radiation In situ experiments X-ray diffraction
1 中国科学院上海应用物理研究所物理与环境科学部, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
3 中国科学院上海高等研究院上海光源科学中心, 上海 201204
X射线扫描相干衍射成像(ptychography)是一种新型的无透镜成像方法,摆脱了传统透镜成像中聚焦元件对分辨率的限制,使理论分辨率只受到X射线波长和探测器数值孔径的限制。然而实验测量中的噪声限制了该方法对成像质量的改善,甚至最终导致图像重建失败。在研究了ptychography现有的相位恢复迭代算法后,本文提出了一种新型的图像重建迭代算法。该算法利用ptychography数据的高冗余性,通过梯度下降最小化技术,在重建样品和探针图像的同时还完成了背景噪声的同步迭代重建,实现了信号和噪声的盲分离功能。通过仿真模拟和实验数据重建,将该方法与传统的迭代算法进行了对比,结果表明新算法能够较好地实现信噪分离,显著提升ptychography的成像质量。
X射线光学 扫描相干衍射成像 信噪分离 背景噪声 相位恢复迭代算法 光学学报
2021, 41(22): 2234001
1 中国科学院上海应用物理研究所上海光源, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
3 中国科学院上海高等研究院上海光源, 上海 201204
基于同步辐射装置的时间分辨X射线铁磁共振方法采用了相移模式的“泵浦-探测”技术,结合了铁磁共振和磁圆二色原理,是研究自旋转移矩和自旋流等自旋电子学问题的一种独特手段。本文介绍了首次在国内第三代同步辐射装置——上海光源发展的皮秒级时间分辨技术以及搭建的X射线铁磁共振实验平台。利用该实验平台,使单层坡莫合金(Ni81Fe19,Py)在2.5 GHz微波磁场的激励下发生铁磁共振,并测量了Ni81Fe19薄膜中Ni元素的电子自旋进动锥角沿光束方向投影随时间的变化曲线。实验结果证明,该实验平台能在GHz量级上激发磁性元素产生电子自旋进动,并且在皮秒级时间尺度上探测到电子自旋进动的振幅和相位。该实验平台的建立能为自旋电子学材料和器件的研究提供独有的技术支持。
X射线光学 同步辐射 时间分辨方法 铁磁共振 自旋进动 光学学报
2021, 41(15): 1534002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Shanghai Advanced Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201204, China
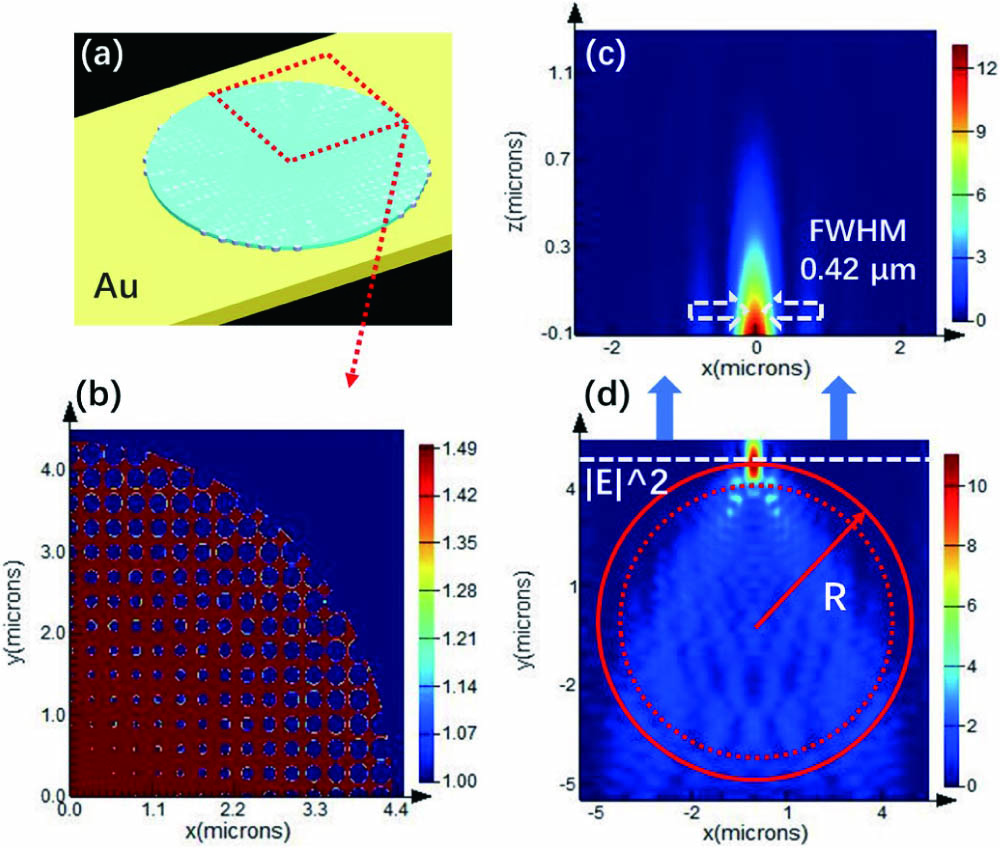
In a single nanoscale device, surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) have potential to match the different length scales associated with photonics and electronics. In this Letter, we propose an accurate design of a plasmonic metasurface Luneburg lens (PMLL) accommodating SPPs. The simulations indicate that the full width at half-maximum is 0.42 μm, and the focus efficiency is 78%. The characters of a PMLL have robustness to manufacturing errors. The PMLL is applied in a 10 μm long compact coupler model, which couples the SPPs to the 40 nm wide output waveguide. The couple efficiency is higher than that of a conventional taper coupler in a broad bandwidth. The design is compatible with standard lithography technology.
Luneburg nano-coupler plasmonics Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(9): 092401
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Shanghai Advanced Research Institute, CAS, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China
2 Shanghai Institute of Applied Physical, CAS, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China
This paper introduces the recent progress in methodologies and their related applications based on the soft x-ray interference lithography beamline in the Shanghai synchrotron radiation facility. Dual-beam, multibeam interference lithography and Talbot lithography have been adopted as basic methods in the beamline. To improve the experimental performance, a precise real-time vibration evaluation system has been established; and the lithography stability has been greatly improved. In order to meet the demands for higher resolution and practical application, novel experimental methods have been developed, such as high-order diffraction interference exposure, high-aspect-ratio and large-area stitching exposure, and parallel direct writing achromatic Talbot lithography. As of now, a 25 nm half-pitch pattern has been obtained; and a cm2 exposure area has been achieved in practical samples. The above methods have been applied to extreme ultraviolet photoresist evaluation, photonic crystal and surface plasmonic effect research, and so on.
soft x-ray EUV interference lithography International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing
2020, 2(1): 012005

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Shanghai Advanced Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201204, China
4 e-mail: wuyanqing@zjlab.org.cn
5 e-mail: tairenzhong@zjlab.org.cn
High-resolution lens-coupled indirect X-ray scintillator imagers are required by many imaging applications. However, the severe weakening of image details prevents its further performance improvement. Through our research, this image degradation is attributed to the broadband loss of the high-spatial-frequency information caused by the high refractive index. A technique known as high-spatial-frequency spectrum enhanced reconstruction is thus proposed to retrieve this information. A two-dimensional high-density array is covered on the scintillator’s exit surface and operates as an encoder based on which high-frequency information can be shifted to the low-frequency region to improve the signal-to-noise ratio. The experimental results show that the middle-high-frequency signal intensities can be increased by an order of magnitude or more, up to times. Therefore, the image details can be effectively enhanced to break through the performance bottleneck of such widely used X-ray imagers for synchrotron radiation facilities or tabletop X-ray tubes.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(7): 07001079
1 中国科学院上海应用物理研究所, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院上海高等研究院,张江实验室,上海光源科学中心, 上海 201204
利用上海同步辐射光源扫描显微光束线站(08U1A)搭建了一套基于荧光发射的低原子序数吸收谱的测量系统,探索部分荧光产额(PFY)的吸收谱方法在软凝聚态(低原子序数元素,原子序数Z<10)和半导体领域的可行性及适用性。以含低原子序数元素的四氟化碳(CF4)气体和半导体样品甲胺铅碘(CH3NH3PbI3)为研究对象验证了PFY吸收谱方法在该系统上的可行性,并确定其样品浓度的测量下限。
X射线光学 低Z元素 低含量元素 荧光发射谱 光学学报
2019, 39(10): 1034002

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Shanghai Advanced Research Institute, Shanghai 201204, China
Achromatic Talbot lithography (ATL) with high resolution has been demonstrated to be an excellent technique for large area periodic nano-fabrication. In this work, the uniformity of pattern distribution in ATL was studied in detail. Two ATL transmission masks with ~50% duty cycle in a square lattice were illuminated by a spatial coherent broadband extreme ultraviolet beam with a relative bandwidth of 2.38%. Nonuniform dot size distribution was observed by experiments and finite-difference time-domain simulations. The sum of the two kinds of diffraction patterns, with different lattice directions (45° rotated) and different intensity distributions, results in the final nonuniform pattern distribution.
220.3740 Lithography 220.4241 Nanostructure fabrication Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(6): 062201
1 中国科学院上海应用物理研究所上海同步辐射光源, 上海 201204
2 东华大学理学院, 上海 201620
提出了一种软X射线荧光吸收谱测试方法。该方法克服了软X射线荧光产率低的问题,消除了荧光自吸收效应,采用部分荧光产额模式获得了材料的软X射线近边吸收结构。使用部分荧光产额模式对钙钛矿太阳能电池的埋藏元素、催化剂的低浓度元素,以及宽禁带半导体进行软X射线近边吸收谱研究。相比全电子产额模式,基于荧光产额模式的软X射线近边吸收结构在材料体相特性、不良导体和低浓度样品测试中更具优势。
X射线光学 荧光光谱 同步辐射 近边吸收结构 软X射线 硅漂移探测器

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201204, China
2 Institute of Functional Nano and Soft Materials (FUNSOM) and Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Carbon-Based Functional Materials and Devices, Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, China
We describe the design and capabilities of the x-ray excited optical luminescence (XEOL) technique at the scanning transmission x-ray microscopy beamline (BL08U1A) of the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility. The detection system is a functional expanding of the original end station, making full use of its precision positioning stages. The simultaneous collection of XEOL and total electron yield spectra is realized using homemade software when the excitation energy is scanned. The setup is validated by the 2D near-edge x-ray absorption spectroscopy (NEXAFS) XEOL mapping across the O K-edge of a nanostructured ZnO sample. The ability to detect the signal of very weak light-emitting material is verified by using TiO2 nanopowder.
Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(Suppl): S23401





